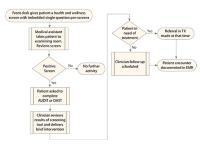
Screening
Why Screen Universally?
- Universal screening normalizes alcohol and substance use questions
- Universal screening avoids stigmatization of those being asked such questions
- Detect current health problems related to at-risk alcohol and substance use at an early stage—before they result in more serious disease or other health problems.
- Detect alcohol and substance use patterns that can increase future injury or illness risks.
- Intervene and educate about at-risk alcohol and other substance use.
- Research has shown that approximately 90 percent of substance use disorders go untreated. (NSDUH, 2007).
Screening can be a significant step toward effective intervention:
- The clinician is often the first point of contact.
- Early identification and intervention lead to better outcomes.
- Patients are often seen by a clinician because of a related physical problem.
Source: Treatnet. (2008). Screening, assessment and treatment planning.
Retrieved from http://www.unodc.org/ddt-training/treatment/a.html
Screening Instruments
The goal of screening is to quickly and efficiently identify patients who may require further assessment or treatment for alcohol and substance use disorders. Screening does not definitively establish diagnosis or treatment needs. In a medical setting, screening typically involves at least two components: biomarkers and patient report. Biomarkers can include a positive drug screen (e.g., urine) or physical indications of possible substance abuse. Patient reports are based on structured or semi-structured questionnaires administered by interview, paper and pencil, or computer. Generally, it is recommended that all agencies within the same health care system use the same screener and administer and score them in the same way.
Numerous substance abuse screening instruments have been developed and are presented below. Substance specific instruments are listed first, followed by instruments that assess for more than one substance.
Alcohol Screeners
CAGE The CAGE Questionnaire asks four questions to assess problematic alcohol use.
- Have you ever felt you should Cut down on your drinking?
- Have people Annoyed you by criticizing your drinking?
- Have you ever felt Guilty about your drinking?
- Have you had a drink, or an "Eye-opener,” first thing in the morning to steady your nerves or deal with a hangover?
An answer of "yes” to any of the four questions indicates need for further assessment.
JA Ewing (1984) ‘Detecting Alcoholism: The CAGE Questionaire’, Journal of the American Medical Association 252: 1905-1907.
Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)
AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test) is a ten-item questionnaire that screens for hazardous or harmful alcohol consumption. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the test correctly classifies 95% of people into either alcoholics or non-alcoholics. The AUDIT is particularly suitable for use in primary care settings and has been used with a variety of populations and cultural groups. It should be administered by a health professional or paraprofessional.
AUDIT-C is a simple 3-question screen for hazardous or harmful drinking that can stand alone or be incorporated into general health history questionnaires.
AUDIT Tool
NIAAA Pocket Screening Guide (Alcohol)
Drug Screeners
Drug Abuse Screening Test (DAST)
DAST(Drug Abuse Screen Test) is a 10-item, yes/no self-report instrument that has been condensed from the 28-item DAST and should take less than 8 minutes to complete. The DAST-10 was designed to provide a brief instrument for clinical screening and treatment evaluation and can be used with adults and older youth.
DAST Tool
Tobacco Screeners
CDC/Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance Survey Questions:
- Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your entire life? NOTE: 5 packs = 100 cigarettes
- Do you now smoke cigarettes every day, some days, or not at all?
Fagerstrom Nicotine Dependence Test
The Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence is a standard instrument for assessing the intensity of physical addiction to nicotine. It contains six items that evaluate the quantity of cigarette consumption, the compulsion to use, and dependence. In scoring the Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence, yes/no items are scored from 0 to 1 and multiple-choice items are scored from 0 to 3. The items are summed to yield a total score of 0-10. The higher the total Fagerström score, the more intense is the patient's physical dependence on nicotine.
Copy of scale and scoring: Fagerstorm Test
Heavy Smoking Index
Simply use the first 2 items of the Fagerstrom. Cut-off >=4 indicates probably dependence.
Multiple Substance Screeners
Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST)
ASSIST (The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test) was developed for the World Health Organization (WHO) by an international group of substance abuse researchers to detect and manage substance use and related problems in primary and general medical care settings.
Assist v3 English
Screening in a Practice Setting